The Impact of Information Shocks in the Dispersion of Betas
This paper studies the impact of public information arrival on the distribution of risk in the stock market over the trading day.
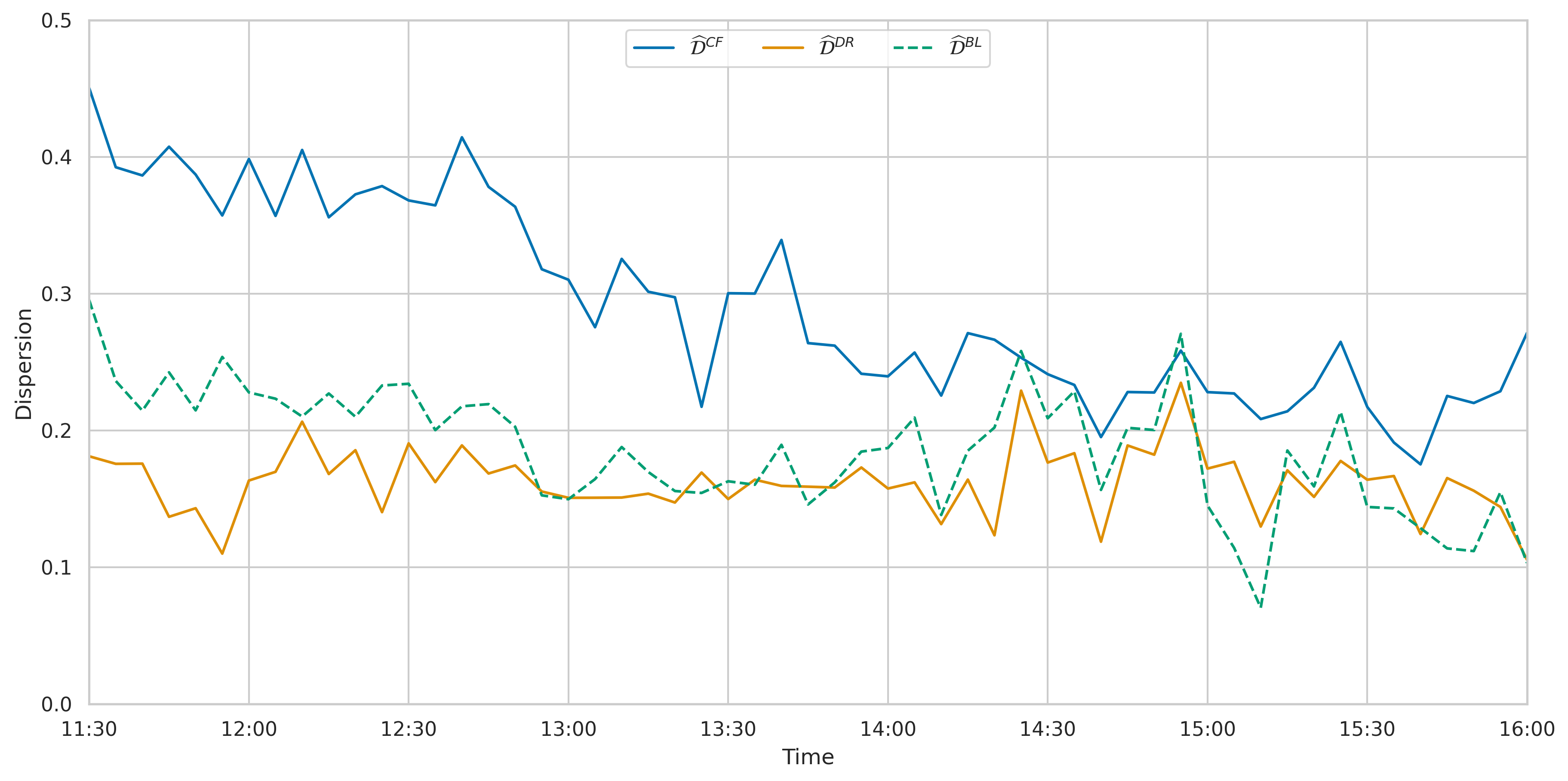
This paper investigates the impact of cash flow and discount rate shocks on the dispersion of CAPM betas in the stock market, using high-frequency returns and real-time news data. The study finds that cash flow shocks, measured through sentiment analysis of news articles, increase beta dispersion due to their heterogeneous impact and spillover effects on the market. In contrast, discount rate shocks do not impact the distribution of risk. Looking at specific types of discount rate shocks we find that it can even decrease dispersion. Controlling for these two sources of information also explains the intraday variation found in (Andersen et al., 2021). The paper also contributes to the literature by introducing a new measure of cash flow and discount rate shocks based on real-time news data, offering a higher degree of precision and frequency than traditional measures. The findings contribute to understanding the factors influencing beta dispersion and the role of news in market dynamics.
References
2023
- Intraday cross-sectional distributions of systematic riskJournal of Econometrics, 2023
2021
- Recalcitrant betas: Intraday variation in the cross-sectional dispersion of systematic riskQuantitative Economics, 2021